Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree is a binary tree in which every node fits a specific ordering property: all left descendents <= n < all right descendents. This must be true for each node n.
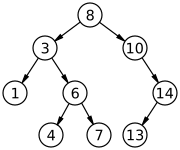
The time complexity of operations on the binary search tree is directly proportional to the height of the tree.
History
BSTs were devised in the 1960s for the problem of efficient storage of labeled data and are attributed to Conway Berners-Lee and David Wheeler.
Time Complexity
The complexity analysis of BST shows that, on average, the insert, delete and search takes O(log n) time. However, in the worst case, they degrade to that of a singly linked list: O(n).
To address the boundless increase of the tree height with arbitrary insertions and deletions, self-balancing variants of BSTs are introduced to bound the worst lookup complexity to that of the binary logarithm.
Self Balancing BSTs
a self-balancing binary search tree (BST) is any node-based binary search tree that automatically keeps its height (maximal number of levels below the root) small in the face of arbitrary item insertions and deletions. These operations when designed for a self-balancing binary search tree, contain precautionary measures against boundlessly increasing tree height.